Carbohydrates: Everyone's guilty pleasure!
Carbohydrates are all these things that everyone likes, SUGARS!! It is one of the MOST crucial components of our survival since we need energy to do many biological processes.
Carbohydrates are classified into groups based on the amount of bonded sugars these groups are monosaccharides, disaccharide, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides are simple (single) sugars.
Disaccharide are two sugars.
Oligosaccharides are 3-10 sugars.
Polysaccharides are complex (many) sugars.
Note: the scientific name of sugar is Saccharide. Hence, the naming Monosaccharide meaning one sugar, Disaccharide meaning two sugars and so on.
Let's circle back to the name. Why is it called a Carbohydrate?
A sugar contains a carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. In fact all carbohydrates have the same molecular formula which is CH2O with the a ratio of 1:2:1. Thus, there will always be twice as much hydrogen as there is carbon and oxygen.
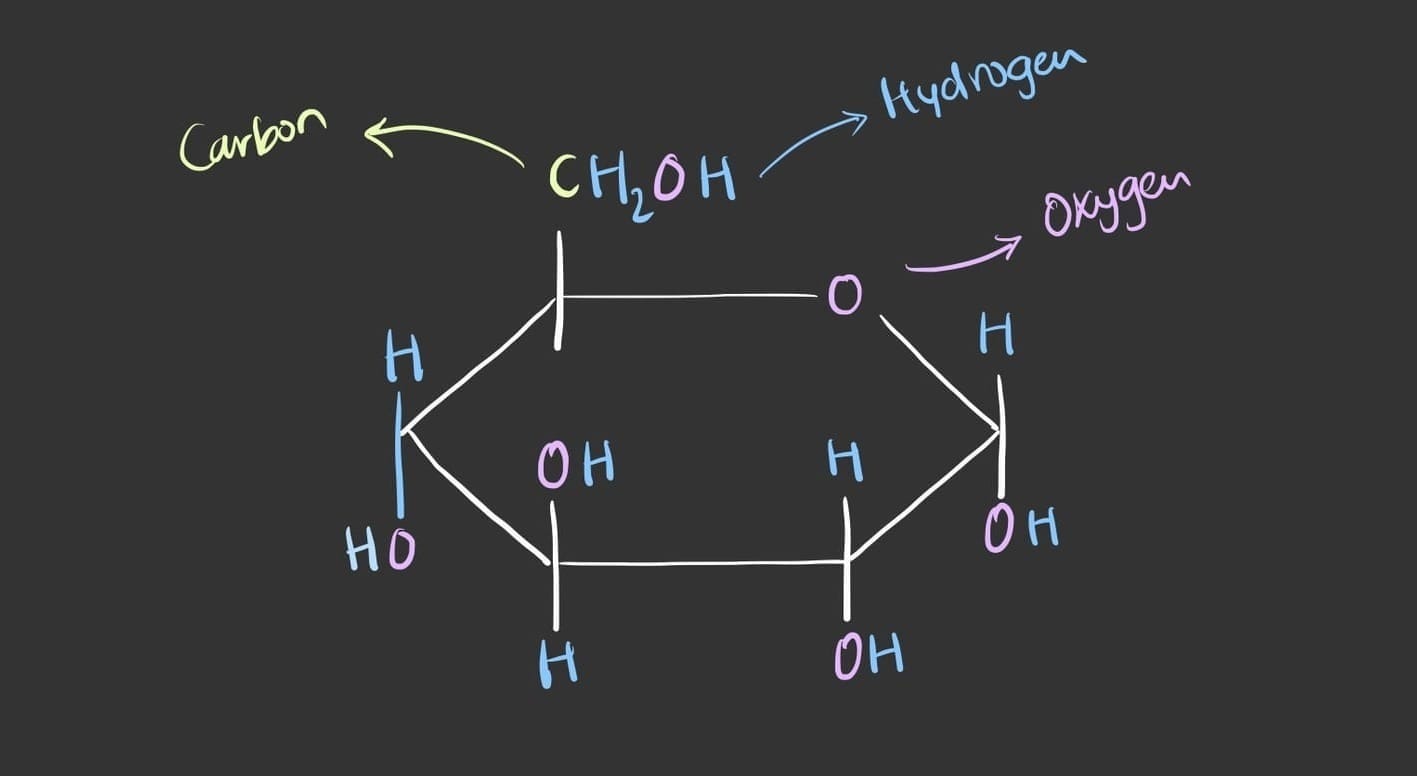
All types of sugars
Now let's learn more about the different types of sugar:
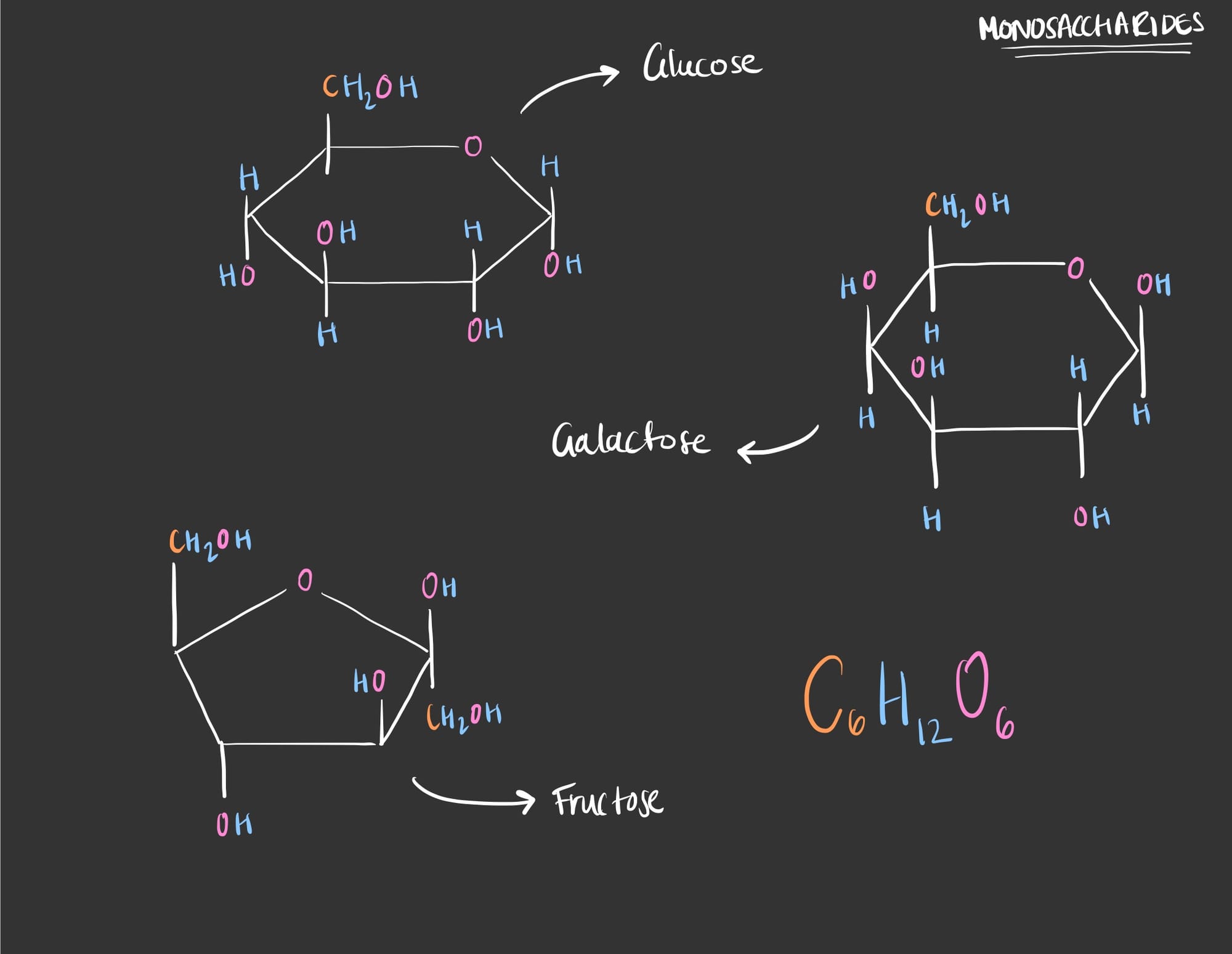
- Starting with the simplest form. Monosaccharides are the simplest form of sugar found in our bodies, it is found traveling through our blood. The three types of monosaccharides are glucose, fructose and galactose.
They all have the same chemical formula which is C6H12O6.
- Glucose is the most known simple sugar that we consume on daily basis.
- Fructose is a much sweeter version of glucose that can be found in fruits and sweeteners.
- Galactose is less sweet and can be found in diary products as it bonds with glucose to produce lactose.
This figure shows the structure of the monosaccharides.
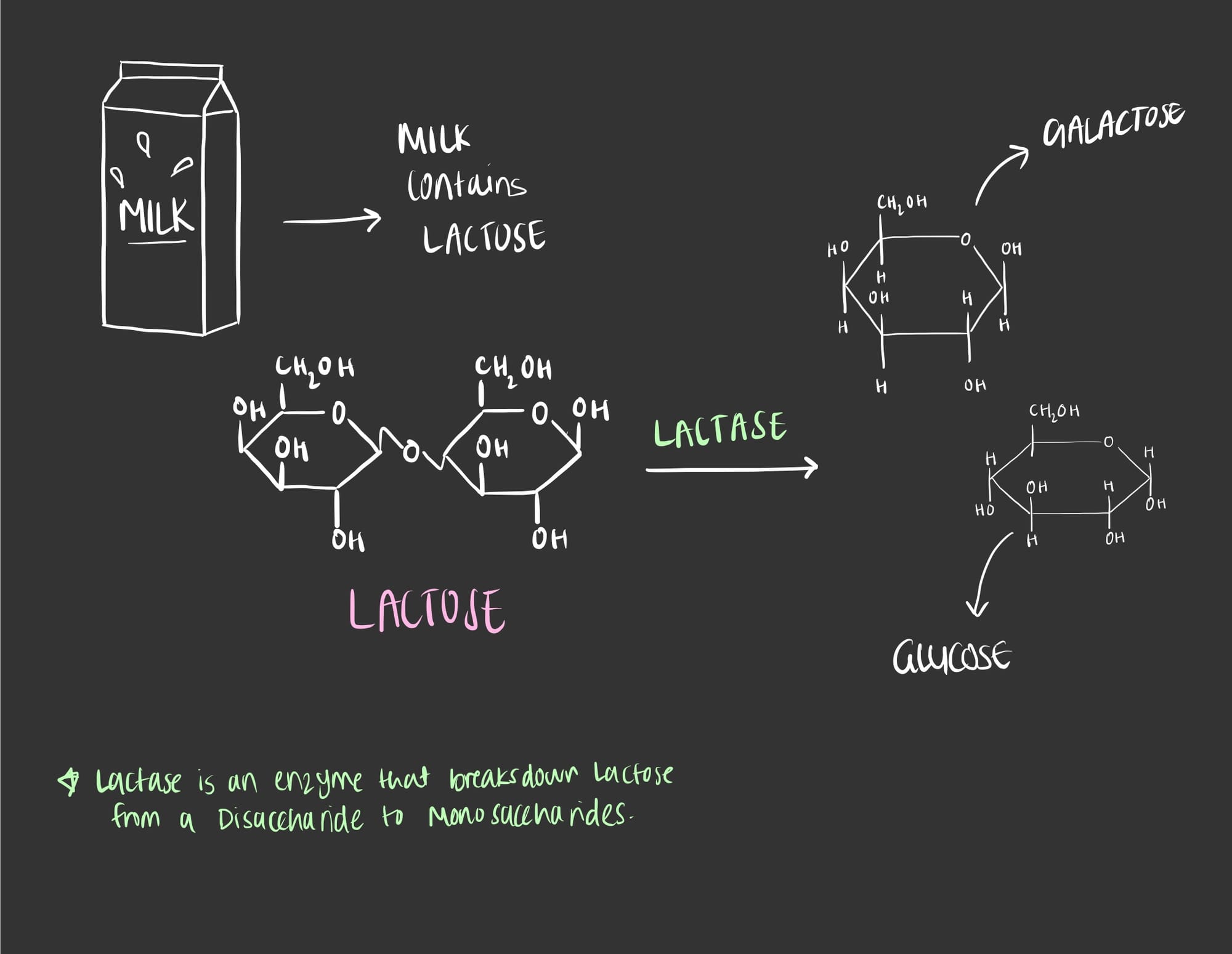
- Disaccharides are the combination of two monosaccharides via chemical bonding known as a glycosidic linkage. It is a covalent bond that occurs between two monosaccharides through a dehydration reaction.
- For example, a bond between glucose and fructose gives us a sucrose which is also known as table sugar. Once sucrose is consumed, it must be broken down via a specific enzyme known as sucrase before being able to travel through the blood and be utilized.
- Similarly, lactose in milk is produced due to the bonding between glucose and galactose and can be broken down via an enzyme known as lactase.
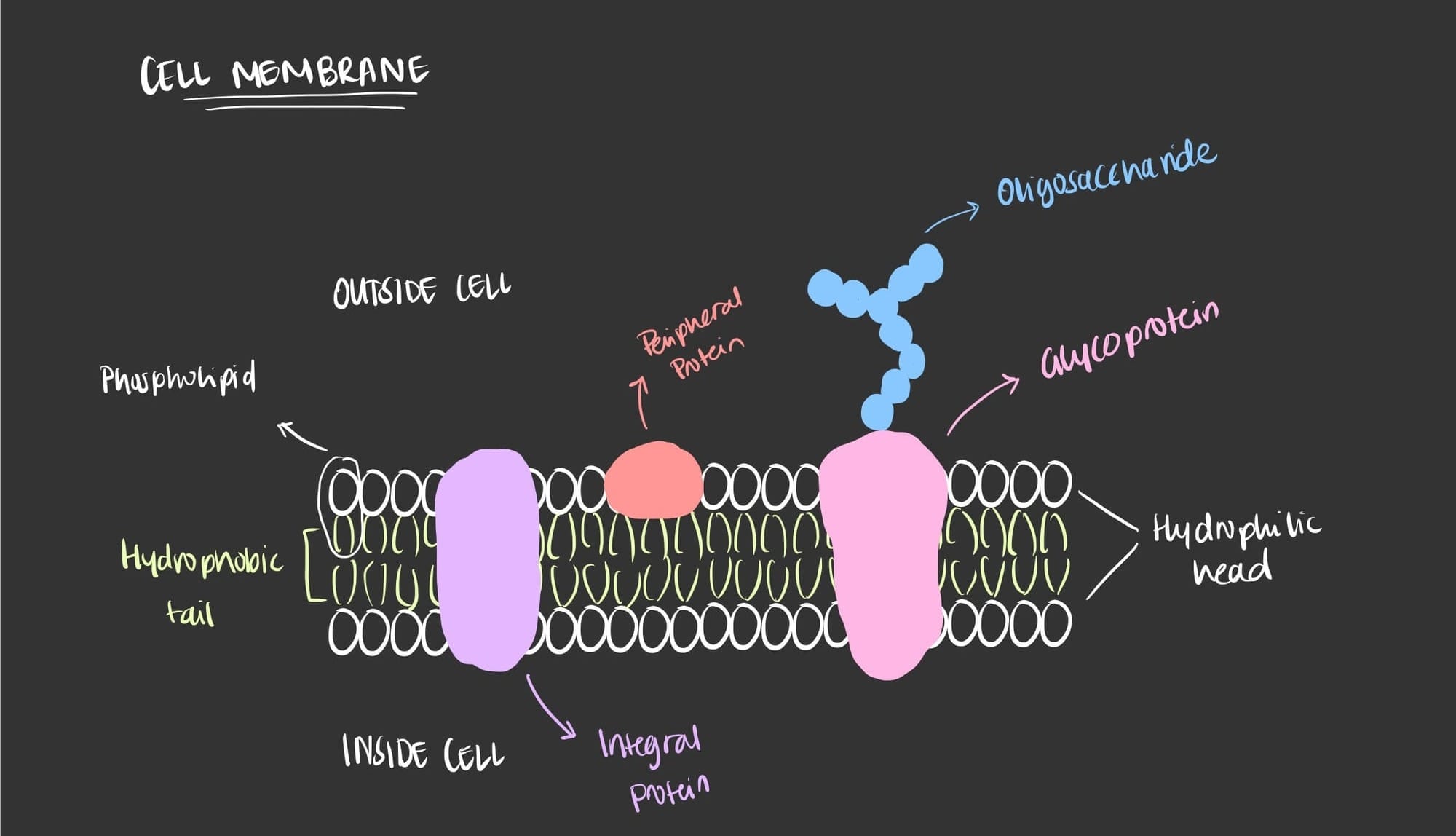
- Oligosaccharides are specifically found on structures present on the cell membrane known as glycoproteins which is sugars + proteins. These glyco structures consist of oligosugars which serve specific functions such as cell signalling and attachment to extracellular matrix.
- Now to the most complex of them all, the polysaccharides. These are essentially hundreds and hundreds of sugars bonded together to create this complex sugar. To fully understand this we will take three examples:
- Plants produce something known as starch which can be found in potatoes but why do plants do that? It is done so plants can store high amounts of energy and access it when it's really required by breaking down the starch into monosaccharides aka glucose.
- Now let's see the same concept but in the human body. Once we consume starches or other sugars, we break them down into it's monosaccharide form and then we bond them over and over again to form a structure known as glycogen which we store in our livers and muscle cells. When sugar levels are low and energy is required the liver breaks down the glycogen to release the monosaccharides, glucose, that can be used by the body.
- Polysaccharides can also be used for structural support. Plants produce something known as cellulose which is a crucial component in the cell wall of plants. In fact, cellulose is what makes the plants' cell walls so tough to breakdown. It is a polymer of glucose that is bonded together to form a long chain known as cellulose. We humans cannot digest it, as in our digestive system can't breakdown cellulose into its monomer form unlike cows that can breakdown cellulose and utilize the glucose.
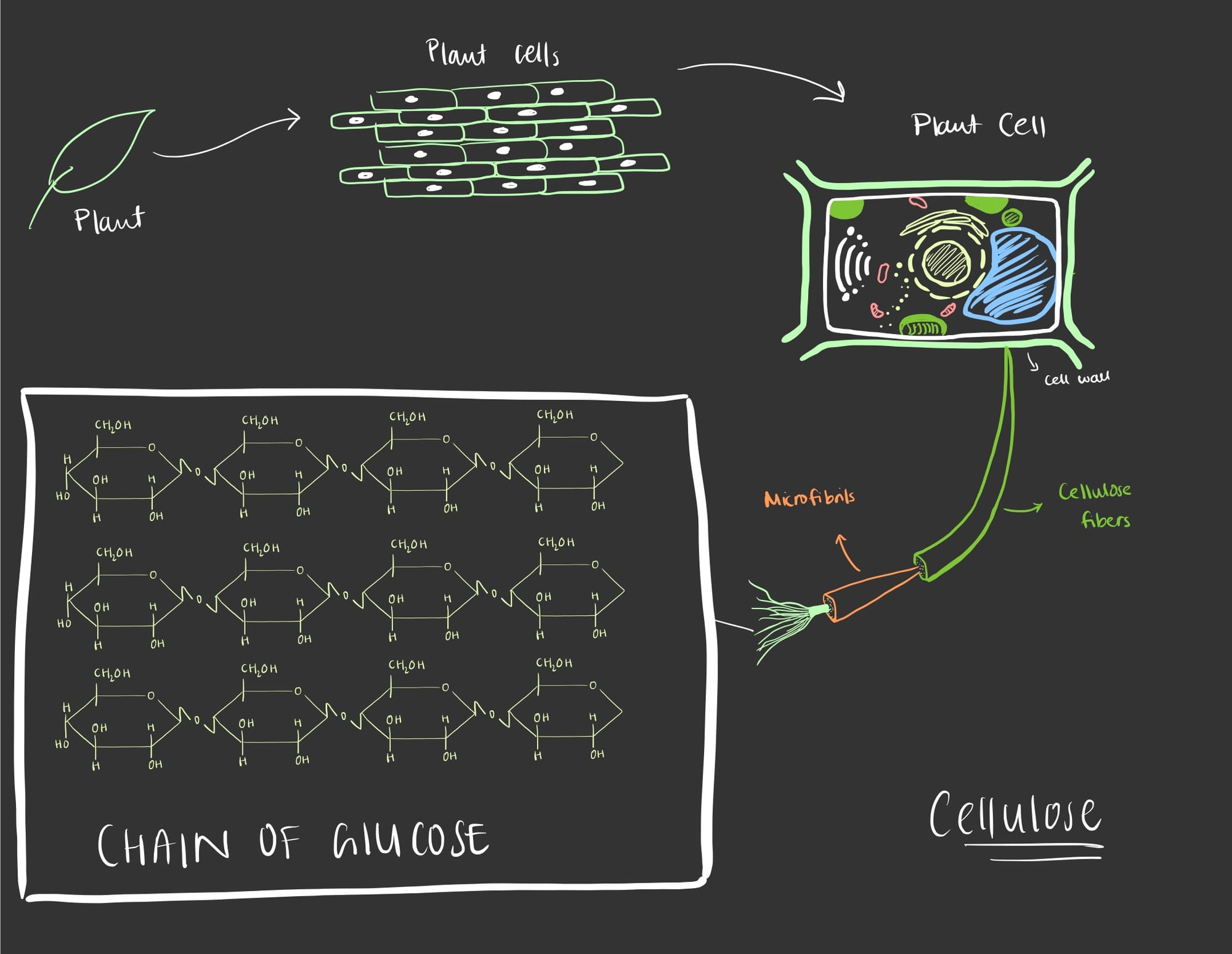
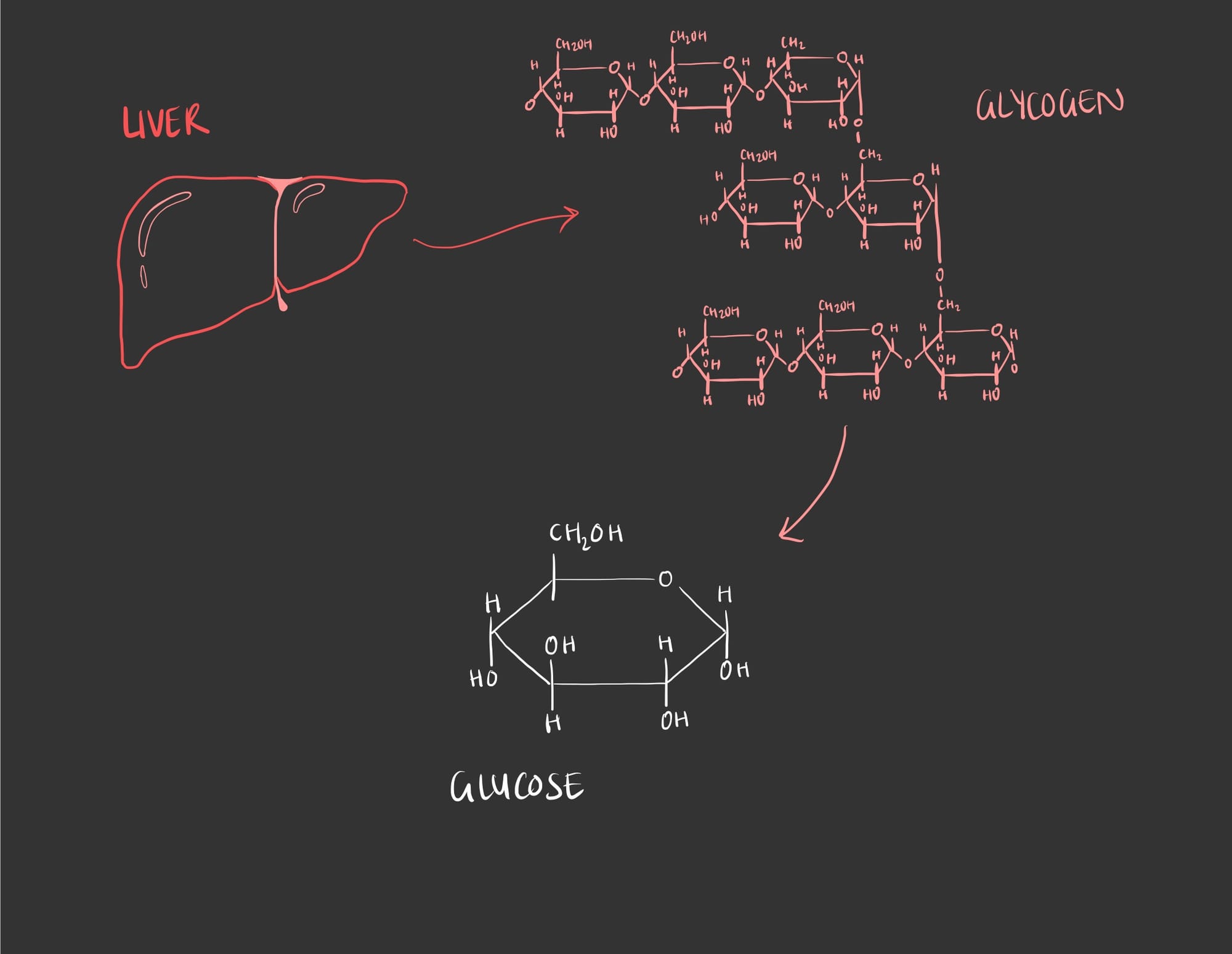
To recap, carbohydrates are sugars and there are many different types of sugars based on the number of sugars from simple to complex. Glucose is one of the most simple forms of sugar while starch and glycogen are one of the most complex. A disaccharide, oligosaccharide and polysaccharide contain more than one sugar that is bonded via a glycosidic linkage through a dehydration reaction. On the other hand, breaking down bonded sugars occurs through a hydrolysis reaction.
