All about Macromolecules
So here we are going to our basics, take a deep breath and let's start with some questions.
- What are the 4 main macromolecules of life?
- What are Macromolecules?
- How are polymers synthesized (or broken down)?
Well, if you answered one of these questions right then you already have a good head start. If not, it’s okay cause I’ll go over them in a bit.
The thing about basics is that sometimes it could be overwhelming but you have nothing to worry about because I am here to break everything down for you!!
What are the 4 main macromolecules of life?
Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids. Macromolecules are significant for the functionality of many biological processes. They are the building blocks of all living organisms and it's absence can have major effects. Macromolecules play pivotal roles in the structure, function as well as regulation of many biological systems. Thus, it's crucial to know and understand such important components because without them we wouldn't function.
What are Macromolecules?
First, let’s break down the word macromolecules, macro- means huge or big and -molecules are groups of atoms. The most simple definition of macromolecules is that they are polymers build from monomers through a process known as polymerisation.
To simply understand the concept let us imagine a lego set where you have small pieces of lego (a monomer) that link together to give you a bigger figure (a polymer). The lego pieces are designed to be linked and unliked to make many different figures.
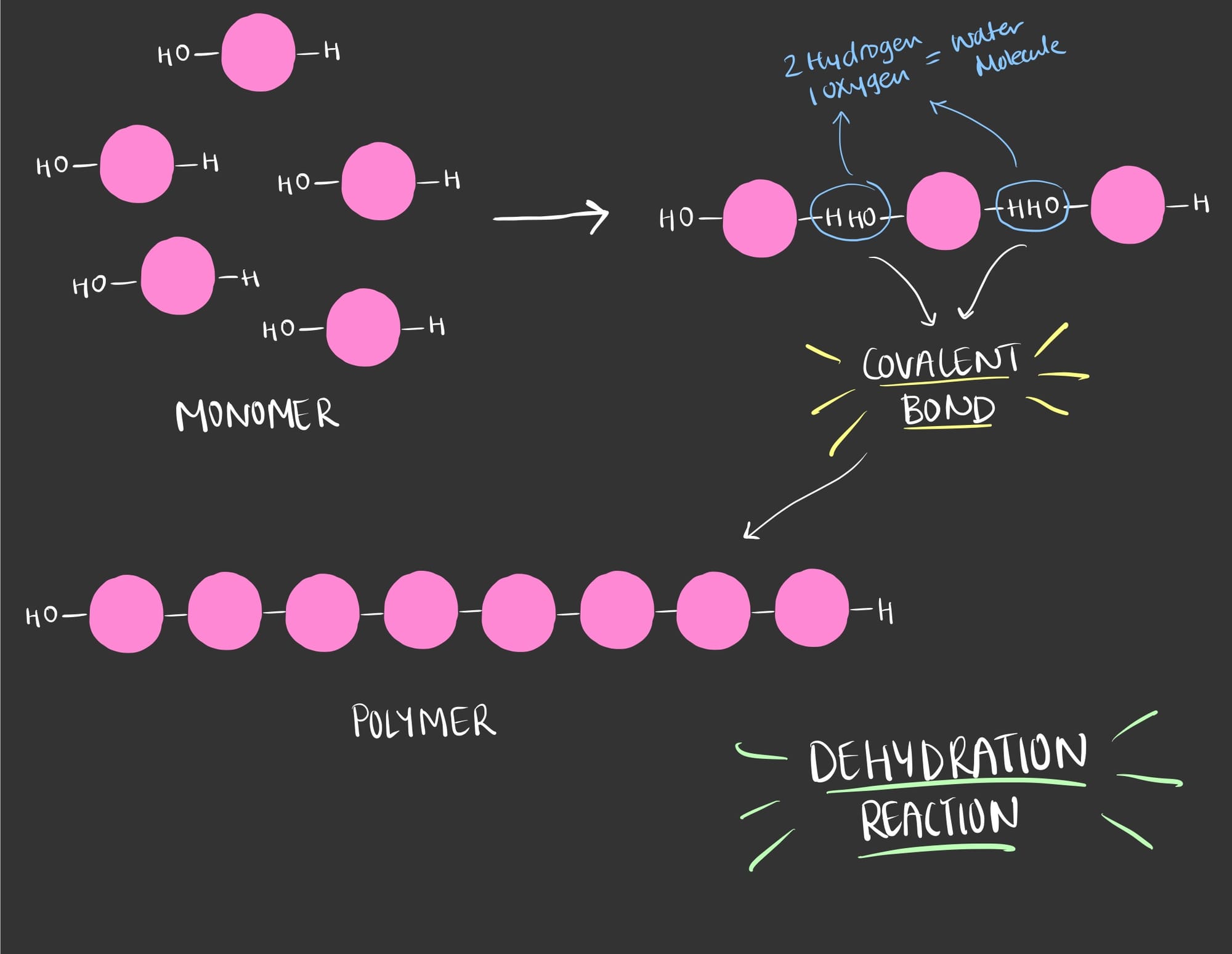
Now let’s connect it, a macromolecule is basically a bunch of monomers linked together via a covalent bond making a polymer.
This part requires a tiny bit of chemistry to understand, but fear nothing because I will simplify everything right about now.
The chemistry behind Macromolecules
How are polymers synthesized (or broken down)?
It's pretty simple, it occurs through 2 simple reactions known as dehydration and hydrolysis. In another simple words it's by either removing or adding water molecules.
To synthesize polymers, a dehydration reaction occurs in which a water molecule is released, but from where did the water come from?
Well a bond occurs between 2 monomers each contributing to the water molecule where one gives a Hydrogen (H) and the other gives a Hydroxyl group (OH).
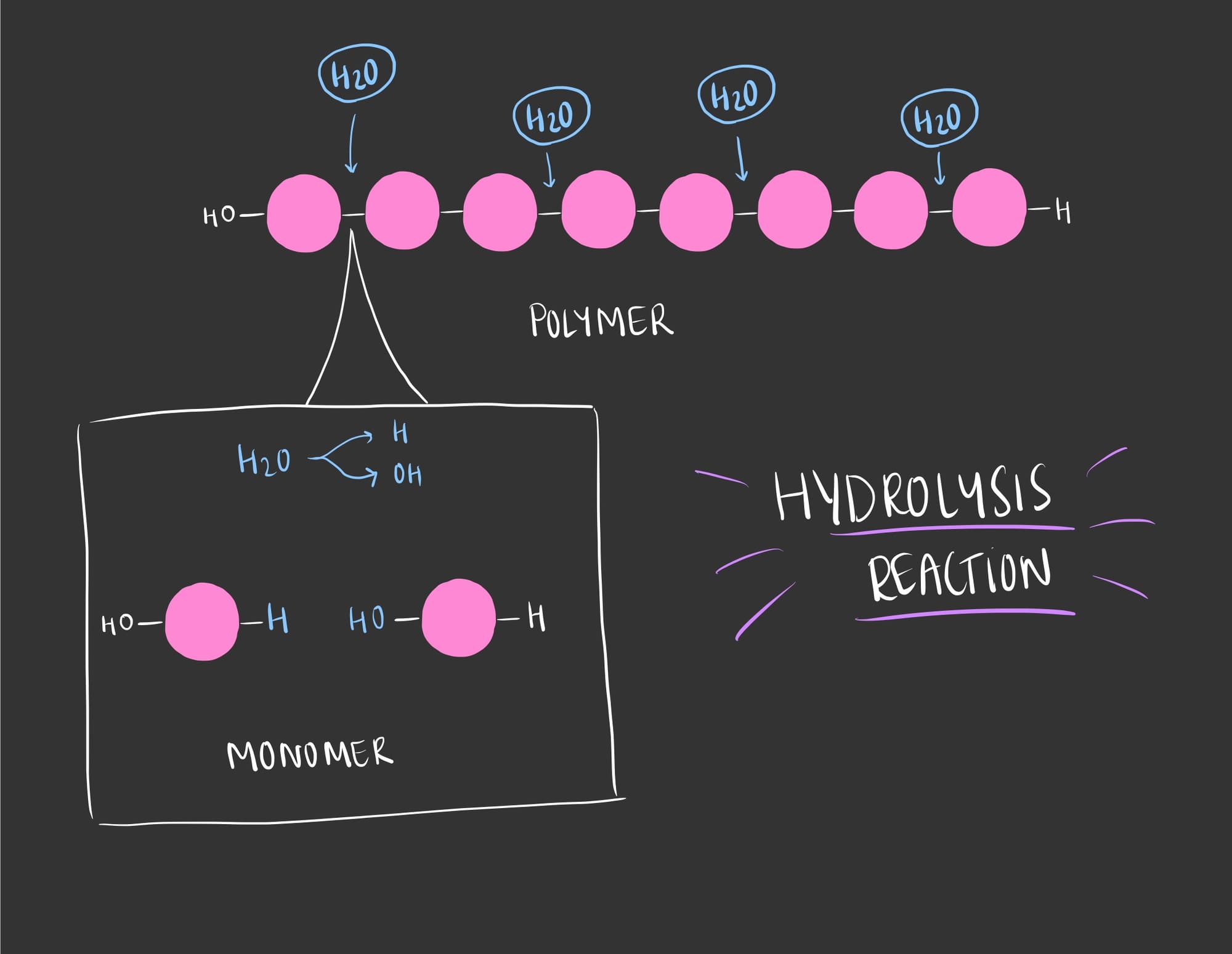
While to breakdown polymers, a hydrolysis reaction occurs in which a water molecule is added between the two bonded monomers, separating them.
Thus, a Hydrogen (H) from the water will attach to one monomer and the Hydroxyl group (OH) will attach to another.
Now that we covered the general idea of what are macromolecules and understood what are monomers and polymers as well as how to form and break them.
Let's go into the 4 categories of macromolecules and discuss each one.
